Este es el nivel English Independent User (B1) del curso de inglés y en esta lección aprendermos el Simple Past.
El Simple Past expresa una acción en el pasado que tiene lugar una vez, nunca, varias veces. También se puede usar para acciones que tienen lugar una tras otra o en medio de otra acción.
Form of Simple Past (Forma de pasado simple)
Examples
- Michael entered a hula hoop contest.
- He won the silver medal.
- She ate the pizza pie.
- The cat slept all day
- Janet studied all night long.
El Pasado Simple (Simple Past) muestra que estás hablando de algo que ya ha sucedido. A diferencia del Pasado continuo (Past Continuous) continuo, que se usa para hablar sobre eventos pasados que ocurrieron durante un período de tiempo, el tiempo pasado simple enfatiza que la acción está terminada.
También puede usar el Pasado Simple (Simple Past) para hablar sobre un estado pasado del ser, como la forma en que alguien se siente acerca de algo. Esto a menudo se expresa con el tiempo pasado simple del verbo to be y un adjetivo, sustantivo o frase preposicional.
Examples
- Michael was proud of his hula hoop victory.
- The contest was the highlight of his week.
- She was full after eating the whole pizza pie.
- The cat was asleep all night.
- Janet was up all night studying.
Cómo formular el pasado simple
Para verbos regulares, agrega-ed a la forma raíz del verbo (o simplemente -d si la forma raíz ya termina en una e.
- Play→Played
- Type→Typed
- Listen→Listened
- Push→Pushed
- Love→Loved
Para verbos irregulares, las cosas se vuelven más complicadas. El tiempo pasado simple de algunos verbos irregulares se ve exactamente como la forma raíz:
- Put→Put
- Cut→Cut
- Set→Set
- Cost→Cost
- Hit→Hit
Para otros verbos irregulares, incluido el verbo to be, las formas pasadas simples son más erráticas:
- See→Saw
- Build→Built
- Go→Went
- Do→Did
- Rise→Rose
- Am/Is/Are→Was/Were
- La buena noticia es que los verbos en tiempo Pasado Simple (Simple Past) (excepto el verbo ser «to be«) no necesitan coincidir en número con sus temas.
How to Make the Simple Past Negative
Afortunadamente, hay una fórmula para hacer que los verbos pasados simples sean negativos, y es igual para los verbos regulares e irregulares (excepto para el verbo ser «to be«). La fórmula es did not + [forma raíz del verbo]. También puede usar la contracción didn’t en lugar de did not para la forma negativa.
Examples
- Michael did enter a hula hoop contest.
- He didn’t win the silver medal.
- She did eat the pizza pie.
- The did cat slept all day
- Janet did not study all night long.
Para el verbo to be, no necesitas que el auxiliar lo did. Cuando el sujeto de la oración es singular, usa el wasn’t o was not. Cuando el sujeto de la oración es plural, usa weren’t o were not.
Examples
- The third-place winner was not as happy as Michael.
- The fourth-place winner wasn’t happy at all.
- The onlookers were not ready to leave after the contest ended.
- The contestants weren’t ready to leave either.
How to Ask a Question (Cómo hacer una pregunta)
La fórmula para hacer una pregunta en tiempo pasado simple es did + [subject] + [raíz del verbo].
- Did Michael win the gold medal or the silver medal?
- Where did Michael go to celebrate?
- Did the judges decide fairly, in your opinion?
Cuando haces una pregunta con el verbo ser, no necesitas que el auxiliar lo haya hecho. La fórmula es was / were + [subject].
- Was Michael in a good mood after the contest?
- Were people taking lots of pictures?
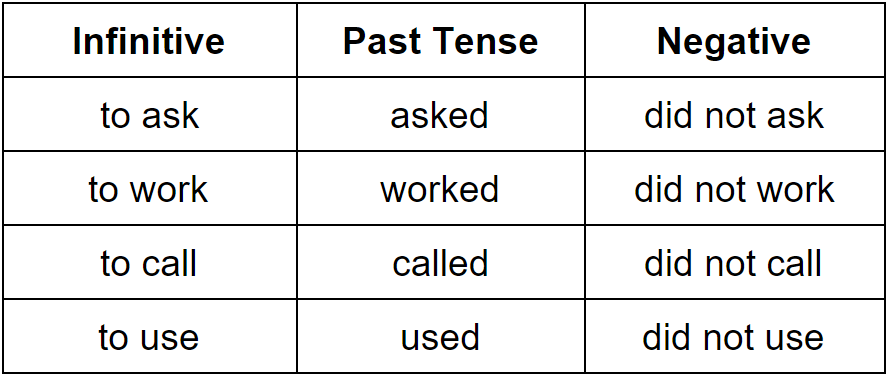
Common Regular Verbs in the Past Tense (Verbos regulares comunes en tiempo pasado)
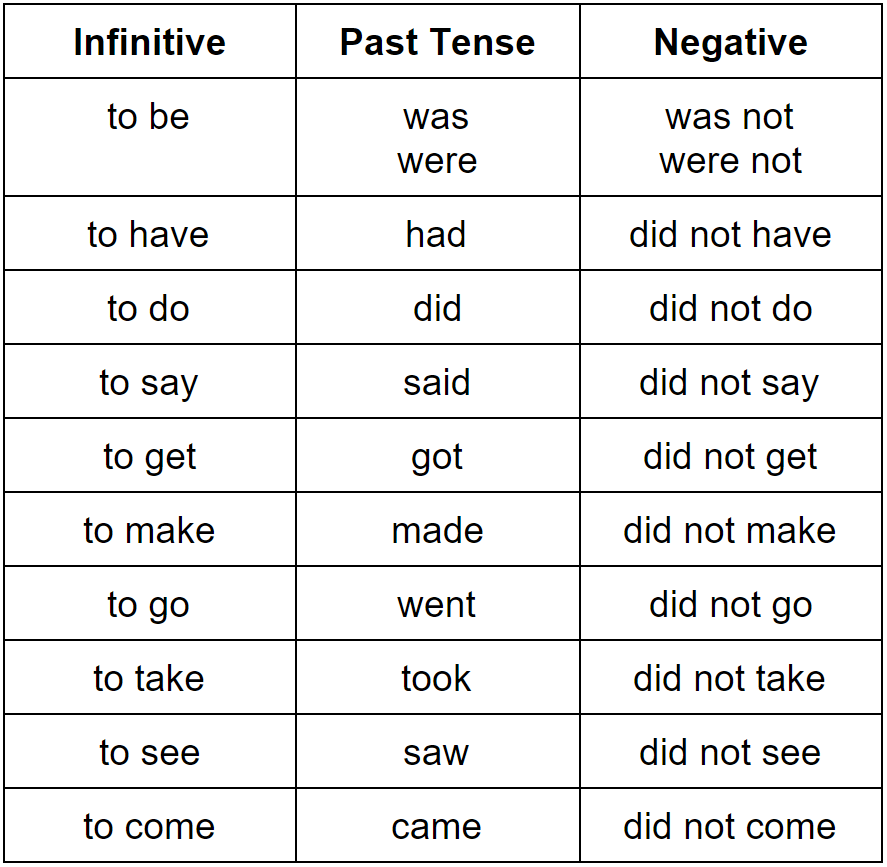
Common Irregular Verbs in the Past Tense (Verbos irregulares comunes en tiempo pasado)
En la próxima lección veremos Past of To Be.